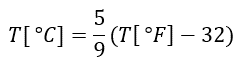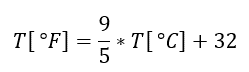Infrared Thermography Dictionary
The field of thermogrpahy is filled with technical terms, jargon, acronyms, and definitions. We hope you find this glossary useful!
Absolute Temperature
Absolute zero is the lowest temperature that can be obtained in any macroscopic system. Absolute temperature means temperature measured on a scale with absolute zero as 0. This is conventionally measured in Kelvin.
Absolute Zero
At absolute zero, a hypothetical temperature, all molecular movement stops. All actual temperatures are above absolute zero. Absolute zero would occur at -273.16 degrees C, -459.69 degrees F, or 0 Kelvin.
Absorption
The process whereby the incident particles or photons of radiation are reduced in number or energy as they pass through matter, i.e. the energy of the radiation beam is attenuated.
Anomaly
The deviation of the value of a parameter, such as temperature, from its average or normal value. Often referenced as a component that indicates impending deterioration as identified by one of the PDM techniques.
Apparent Temperature
The uncompensated reading from an IR camera where emissivity is set to 1.0 and distance is set to 0.
ASNT
The American Society for Nondestructive Testing (NDT). The organization of NDT professionals offers many services and products of interest to the NDT community.
ASTM
American Society for Testing and Materials. An organization to establish test standards for materials, products, systems, and services for a wide range of materials.
Atmospheric Attenuation
A decrease in the intensity of infrared radiation due to absorption and scattering in the atmosphere. Most common factor for thermography is humidity.
Auto Image Adjust
Automatic camera or software function that adjusts Level and Span based on image content.
Background Temperature
The temperature of objects reflected by the target.
Baseline Data
Thermal data collected when a component is considered by the Condition Based Maintenance group to be in optimum operating condition which serves as a basis for comparison of future thermal data during analysis activities.
Black Body
A theoretical object that radiates the maximum amount of energy at a given temperature, and absorbs the entire energy incident upon it.
Calibration
The process whereby the magnitude of the output of an infrared camera is related to the magnitude of the input radiation from black body references.
Calibration Check
A formal check of the radiometric accuracy of the imaging system performed by comparing its measured value to that of a known reference source, typically a human tear duct or a calibrated black body reference device.
Celsius
A temperature scale in which zero degrees is the freezing point of water and 100 degrees is the boiling point. Conversion to Celsius from the Fahrenheit temperature scale is by the following formula:
T[°C] = Temperature in degrees Celsius, T[°F] = Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit . For IR inspections it is common sense to use the Centigrade scale instead of the Fahrenheit scale.
Certification
A process by which an agency/organization validates, based upon predetermined standards, an individual thermographer’s qualifications and knowledge for practice in a defined application.
Certified
Written documentation of qualification.
Color Palette
Scheme that assigns colors to various image gray levels.
Condition Based Maintenance
An equipment maintenance strategy based on measuring the condition of equipment in order to assess whether it will fail during some future period, and then taking appropriate action to avoid the consequences of that failure.
Conduction
The transfer of heat energy through a substance or from one substance to another by direct contact of atoms or molecules.
Convection
Transport of heat by the movement of a fluid. Wind is the most common factor for thermography applications. Convection removes heat from thermal anomalies – known as convective cooling.
Delta T
The temperature difference between two targets or locations, usually of comparable targets under comparable conditions.
Diffuse Reflection
The random reflection from a rough surface, which results in a fuzzy, scattered reflection.
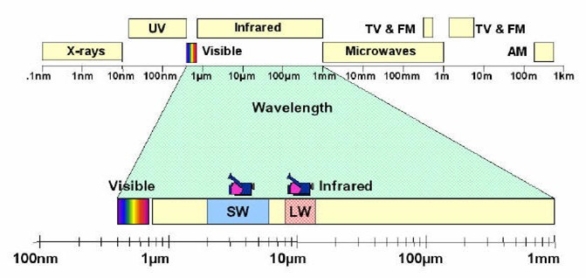
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The ordered series of all known types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged by wavelength ranging from the short cosmic rays through gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, visible radiation, infrared radiation, microwaves, to the long wavelengths of radio energy.
LW = Long Wave = High band
SW = Short Wave = Low Band
Emissivity
The ratio of energy emitted by an object to the energy emitted by a black body at the same temperature.
Fahrenheit
Temperature scale based on 32 degrees F for the temperature at which water freezes and 212 degrees F for the temperature at which water boils: (180 differential temp). Conversion to Fahrenheit from the Celsius temperature scale is by the following formula:
T[°C] = Temperature in degrees Celsius, T[°F] = Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit . For IR inspections it is common sense to use the Centigrade scale instead of the Fahrenheit scale.
Failure Mode
Effect by which failure is observed.
Field of View (FOV)
The largest area that your imager can see at a set distance. Typically this value is indicated by the opening angle of the IR camera. Separate values are given for horizontal and vertical opening.
Focus
Maximum clarity or distinctness of an image rendered by an optical system; “in focus”, “out of focus.”
Forced Convection
Convection aided by wind or mechanical means such as a pump or blower.
FoRD – Focus, Range and Distance
Thermal imager parameters that normally cannot be adjusted in IR software, hence must be correct before an image is saved, or the readings will be compromised.
Hazardous Locations
Locations where fire or explosion hazards may exist due to flammable gases or vapors, flammable liquids, combustible dust or ignitable fibers.
Heat
A form of energy that is transferred by a difference in temperature.
Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a specific quantity of a substance by one degree.
Heat Transfer
The process of thermal energy flow from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature via conduction, convection, and/or radiation.
IEC
International Engineering Consortium.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
Instantaneous Field of View (IFOV)
A camera specification that describes the smallest object that can be seen at a given distance using a camera with a given lens. Also known as spatial resolution. The IOFW is usually given in mrad (milliradians).
Instantaneous Field of View Measurement (IFOV)
A camera specification that describes the smallest size object that can be measured at a given distance using a camera with a given lens or measurement spot size.
Incident Radiation
The total radiation going to an object.
Indirect Measurement
A situation where the source of heating is buried far away from the surface being viewed by the IR camera, resulting in a much lower temperature.
Infrared
Infrared (IR) radiation is electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength that is longer than visible light, but is shorter than microwave radiation. The name means “below red” (from the Latin infra, “below”) red being the color of visible light of the longest wavelength. Infrared radiation spans three orders of magnitude and has wavelengths between 0.7 µm and 1000 µm (1 mm).
IR Technician
Person conducting the IR inspection.
Inspection
The examination of the condition of a system by an expert.
Insulation
Any material that offers resistance to heat transmission. When insulation is placed in walls, ceilings or floors it reduces the loss or gain of heat from outside sources.
ISO
International Organization for Standardization.
Isotherm
A measurement tool that highlights areas of equal apparent temperature.
Kelvin
A unit of temperature equal in size to the Celsius degree, but with the zero set by the absolute zero of temperature, -273.15 degrees Celsius. Ice will melt at 273.15 Kelvin, room temperature is about 293 degrees Kelvin, and water boils at 373.15 Kelvin, at sea level. Average human body temperature is 310 degrees Kelvin. Kelvin is used to measure absolute temperatures and temperature differences (see under Temperature Differences). According to international standards, Kelvin should be used to indicate temperature differences rather than °C or °F.
Level
Thermal “brightness” adjustment on an infrared camera.
Load
The amount of electric power or energy delivered or required at any specified point or points on a system.
Long Wave (LW)
Infrared energy in the region from 8 – 13 µm.
Natural Convection
Heat transfer between a surface and adjacent fluid (usually air) and by the flow of fluid from one place to another, induced by temperature differences rather than by mechanical means, also called free convection. Compare with forced convection.
NEMA
National Electrical Manufacturers Association.
Newton’s Law of Cooling
Newton’s Law says that the time a substance takes to cool off depends on the temperature difference between the substance and the surroundings.
Opaque
Impervious to radiant energy. In thermography, an opaque material is one that does not transmit thermal infrared energy. Thermally opaque materials include glass, plexiglas, and metal.
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
P1
Proactive Domain – Earliest stage on the p-f curve. Defect entered the equipment, but the equipment will still run for several months. Further investigation is warranted.
P2
Predictive Domain – Middle stage on the p-f curve. Defect has further developed. Equipment is still working, but failure cannot be excluded in due time. Repair is warranted. Equipment should be monitored until repair.
P3
Protective Domain – Last stage on the p-f curve. Equipment is close to failure. Immediate repair is warranted.
Personalized Protective Equipment (PPE)
Safety devices or safeguards worn by workers to protect against environmental hazards. PPE includes helmets, safety goggles, hearing protectors, face shields, respirators, arm guards, smocks, gloves, and safety boots.
Potentially Hazardous Work
Tasks which in the absence of appropriate controls have a high potential for causing serious injury or death. These include, but are not limited to: electrical repair hot work (live) and electrical diagnostic hot work (live) on systems or equipment above nominal 50 volts and potentially hazardous switching.
Prohibited Approach Boundary
An approach limit at a distance from an exposed live part within which work is considered the same as making contact with a live part.
Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
Periodic equipment condition monitoring and diagnostics to increase the availability of plant equipment, reduce maintenance cost, and increase personnel safety.
Pyrometer
Any instrument used for temperature measurement. A radiation or brightness pyrometer measures visible energy and relates it to brightness or color temperature. An infrared pyrometer measures infrared radiation and relates it to target surface temperature.
Qualification
Demonstrated skill, knowledge, documented training, and documented experience for thermography applications.
Qualified
Personnel having suitable training and documented experience, and having passed suitable written and practical examinations to perform the defined task.
Qualified Electrical Escort
Site approved licensed electrician other than the thermographer with CPR certification or someone capable of getting a trained CPR person to the testing location within 4 minutes of an incident.
Qualified Person
A qualified person is a person that is:
- Knowledgeable of the construction and operation of the equipment to be worked on, accessed, inspected or tested.
- Skilled and knowledgeable in the use of the work methods for performing the task.
- Understanding of the hazards associated with the equipment.
- Familiar with potential injuries that may occur from the hazards and other undesirable consequences.
- Able to recognize the hazards.
- Distinguish live parts from de-energized parts
- Determine the voltage level
- Determine the degree and extent of the hazard
- Able to avoid the hazards.
- Knowledgeable of and skilled in the use of the safe work practices required for the task without incident or injury
- Knowledgeable of the approach distances to energized components
- Knowledgeable of the local mandatory (legal) requirements.
Qualitative
Indicative only of relative magnitudes, rather than their numerical values. A qualitative comparison would say whether one thing is hotter, cooler, or the same temperature to another, without specifying the magnitude of any difference.
Quantitative
A quantitative property can be meaningfully measured using numbers. Properties which are quantitative properties such as assigning a numeric value to a measurement include: the temperature of a tire and the time for a hammer to fall a certain distance.
Radiation
Energy transport (such as heat) through electromagnetic waves.
Range
The lowest and highest temperatures that can be imaged and/or measured with an IR camera’s detector setting. Most cameras have several overlapping ranges.
Reflected Apparent Temperature
The apparent temperature of objects whose radiant energy is reflected off the target into the IR camera.
Reflectivity
The proportion of incident radiation reflected by a surface, expressed as a fraction or percentage.
Relative Humidity
The ratio of water vapor contained in the air compared to the maximum amount of moisture that the air can hold at that particular temperature and pressure.
Repeatability
The capability of an instrument to exactly repeat a reading on an unvarying target over a short or long-term time interval. For thermal measurements, expressed in ± degrees or a percentage of full scale.
Report
A written document describing the findings of your Infrared (thermal) imaging scan. See “sample“.
Resolution
Clarity or fineness of detail; used to denote the total number of pixels in a displayed image. A high-resolution camera can render fine details with greater sharpness than a low-resolution system.
Resistance Temperature Device (RTD)
A sensor that measures temperature by a change in resistance of the sensor as a function of temperature.
Route
A path which is planned and followed regularly with equipment to be inspected along the way.
Severity Classification Criteria
A means for ranking thermal anomalies for repair priority.
Short Wave (SW)
Infrared energy in the region from 1.8 – 2.4 µm.
Solar Loading
Heat added to objects by the sun, that is not self-generated due to a problem, also known as Solar Gain or Thermal Gain.
Span
Thermal “contrast” adjustment on an IR camera. Adjusting the span will change the temperature span between black and white on an image.
Spatial Resolution
The clarity of a single image or the measure of detail in an image.
Specular Reflection
A mirror-like reflection.
Spot Pyrometer
A pyrometer is a non-contact temperature measuring device.
Spot
The instantaneous size (diameter unless otherwise specified) of the area at the target plane that is being measured by the instrument. In infrared thermometry, this is specified by most manufacturers to contain 95% of the radiant energy of an infinitely large target of the same temperature and emissivity.
Spot Size Ratio
Ratio of the distance from an IR camera to an object compared to the size of the spot being measured (also called D:S ratio). (Spot size ratio)(Minimum target size) = Maximum viewing distance.
Temperature Differences
The International System of Units (SI) defines the unit of temperature differences by the expression of Kelvin (K). This means the difference of the absolute temperature T1 = 20°C and T2 = 45°C is Δϑ = 25K. Note: The absolute temperature T3 = 25K would be equal to T3 = 248,15°C.
Thermogram
A thermal map or image of a target where the gray tones or color hues correspond to the distribution of infrared thermal radiant energy over the surface of the target. When correctly processed and corrected, a graphic representation of surface temperature distribution (quantitative Thermogram).
Thermography
Thermography is the art and science of utilizing infrared sensing devices to determine the surface temperature distribution of a device that may not be readily accessible. Typically, an infrared video camera is used, and the video image is digitized and fed into a computer that assigns different colors to different temperatures so one can see at a glance if there are hot spots in the device. Thermography is extensively used to check electrical breaker panels, fuses, etc., for local heating.
Trending
Comparison over time of data on same equipment.
True-RMS Corrected Ammeter
An ammeter capable of measuring harmonic loads.
Unqualified Person
A person who has only received basic awareness training on electrical systems. This person must remain outside the Limited Approach Boundary and must not cross the Flash Protection Boundary unless wearing the appropriate PPE and is escorted by a qualified person. At no time can an unqualified person cross the Restricted Approach Boundary.
UNQUALIFIED PERSON – Examples
- Unqualified persons shall not open, pry a, or otherwise try to gain access to any MCC (motor control center) container, box, can or cabinet for the purpose of resetting or restarting any electrical equipment.
- Management personnel or hourly employees who are not documented as being a qualified person shall not work on, with, near or around any live exposed electrical parts.
- Unqualified persons cannot enter the Flash Protection Boundary or Shock Limited Approach Boundary unless escorted by a qualified person.
Work Near
Work that is near enough to exposed energized parts for employees to be exposed to any hazard they present.
Work On
Work performed on exposed energized parts, involving either direct contact or contact by means of tools or materials, which include diagnostic work (only qualified persons may perform this type of work).
Written Practice
The document that states how personnel are qualified and certified to perform infrared inspections.